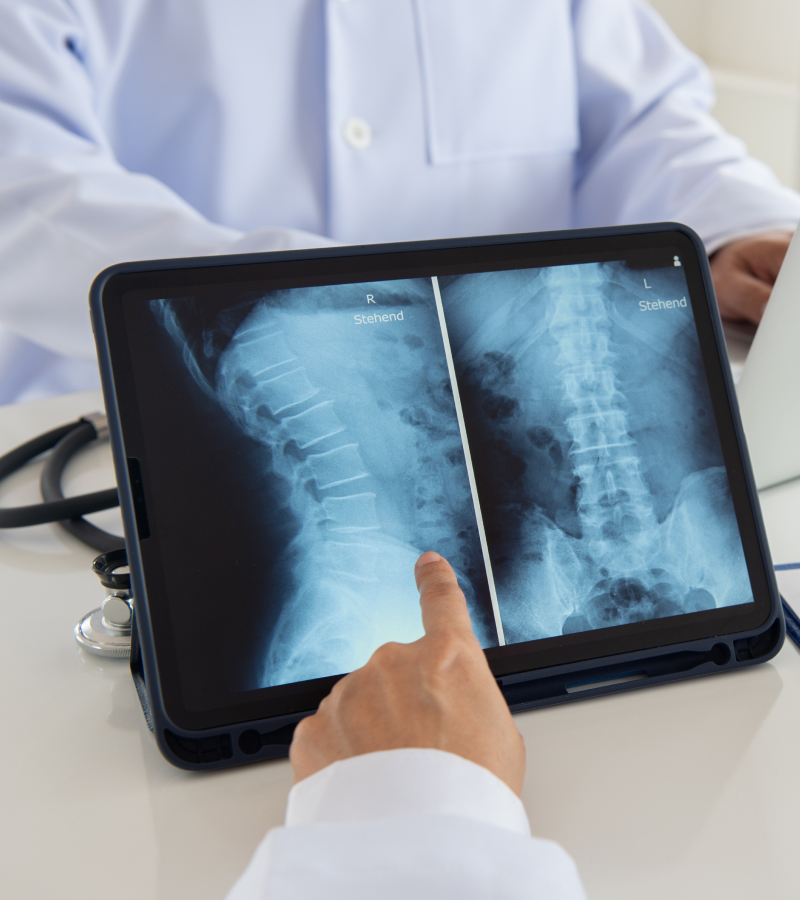
Conventional (open) spine surgery involves dissecting the spinal muscles from their attachments and retracting them in order to reach the spine. This causes injury (Denervation/ Ischemic) and affects post-op muscle function.
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery (MISS) or Lumbar Discectomy is a type of technique wherein the entire spine surgery is done through small tubular retractors without disrupting the muscular attachments of the spine.
This procedure involves the removal of the herniated or prolapsed disc that is pressing on the nerve root, thereby providing relief from pain and discomfort. This surgery can be done as an open (conventional) technique or a minimally invasive (Key-hole; Muscle sparing) technique.
There are different types of minimally invasive techniques. When the discectomy is done using a Tube (Tubular retractor), it is referred to as ‘Tube Assisted Minimally Invasive Lumbar Discectomy.’ Irrespective of the Minimally Invasive nature of the surgery, consulting with a spine specialist can ensure that the primary goal (Nerve root decompression and disc fragment removal) is not compromised.